Role of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Modern Ophthalmology
In recent years, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has revolutionized the field of ophthalmology, offering an advanced, non-invasive method to visualize the detailed structure of the retina and other layers of the eye. With its ability to capture high-resolution images, OCT has become an indispensable tool for diagnosing and managing a wide range of eye conditions. This blog explores the significant role OCT plays in modern ophthalmology, highlighting its applications, benefits, and how it enhances patient care.
What is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)?
OCT is an imaging technique that uses light waves to take cross-sectional images of the retina and other structures inside the eye. It functions similarly to an ultrasound, but instead of sound waves, OCT uses light to produce detailed images. The technology has evolved significantly since its inception, and now, with advancements like Swept-Source OCT and OCT Angiography, ophthalmologists have a comprehensive toolset to assess eye health in real-time.
Key Applications of OCT in Ophthalmology
1. Retinal Disease Diagnosis and Management
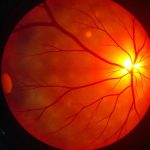
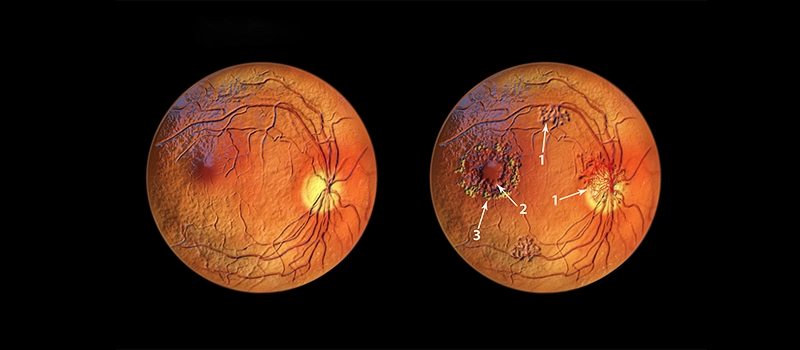
One of the most important roles of OCT is in the diagnosis and management of retinal diseases. Conditions like macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and macular edema can cause significant vision loss, but OCT has greatly improved early detection and monitoring.
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): OCT can help detect early changes in the macula, even before visible symptoms arise. This is crucial for treating dry and wet forms of AMD, which can lead to irreversible vision loss if not managed promptly.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy can cause damage to blood vessels in the retina. OCT is invaluable in tracking the development of retinal thickening or edema, which is a major indicator of diabetic retinopathy. This allows for timely interventions and treatments such as laser therapy or anti-VEGF injections.
- Macular Edema: OCT helps monitor the presence and extent of fluid accumulation in the macula, providing insights into the severity of the disease and guiding treatment options.
2. Glaucoma Diagnosis and Monitoring
Glaucoma, a group of eye conditions characterized by damage to the optic nerve, is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide. OCT is especially helpful in detecting glaucomatous damage to the optic nerve and monitoring its progression.
- Optic Nerve Head (ONH) Imaging: OCT allows for high-resolution imaging of the optic nerve head, helping ophthalmologists assess the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and other structures, which are crucial indicators of glaucoma damage.
- Macular Ganglion Cell Layer Analysis: OCT can also measure the ganglion cell layer in the macula, a crucial area for visual function, to detect early signs of glaucoma before significant optic nerve changes occur.
3. Corneal Imaging and Surgery Planning
OCT is also widely used for imaging the cornea, particularly before and after corneal surgeries. This is essential for procedures like LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) and corneal transplants. OCT helps in pre-operative assessments by providing detailed images of the corneal thickness, shape, and structure, ensuring the surgeon can plan the procedure with precision.
Moreover, OCT is crucial for monitoring the healing process post-surgery, tracking potential complications such as epithelial defects or corneal scarring.
4. Retinal Surgical Planning and Monitoring
OCT is indispensable in planning and monitoring the outcomes of retinal surgeries, including vitrectomy and retinal detachment repair. It provides surgeons with a detailed view of the retina, allowing them to assess the extent of damage or detachment. Post-surgical OCT images help track the recovery process and detect any recurrence of problems, ensuring better outcomes for patients.
5. OCT Angiography (OCTA)
OCT Angiography is an advanced application of OCT that provides non-invasive imaging of the retinal blood vessels. Unlike traditional dye-based angiography, which requires injecting a contrast agent into the bloodstream, OCTA uses light waves to capture detailed images of blood flow in the eye.
This technology is particularly useful in detecting conditions like diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, and other vascular disorders, enabling earlier detection and more precise treatment planning.
Benefits of OCT in Ophthalmology
1. Non-invasive and Painless
OCT is non-invasive, meaning it doesn’t require any needles, injections, or incisions. The procedure is painless and quick, making it an ideal diagnostic tool for both adults and children. Patients do not need to undergo any special preparations, and the images can be obtained in a matter of minutes.
2. High-resolution Imaging
OCT provides incredibly detailed, high-resolution images of the eye, which allow for early detection of even the smallest abnormalities. This high level of precision helps ophthalmologists diagnose conditions at their earliest stages, leading to better treatment outcomes.
3. Real-time Imaging
One of the standouts features of OCT is its ability to provide real-time images. This allows ophthalmologists to make immediate decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment, improving the overall efficiency of eye care.
4. Monitoring Disease Progression
For chronic conditions like glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, OCT is invaluable in monitoring disease progression. By comparing OCT images taken over time, ophthalmologists can track any changes or deterioration in the eye’s structures, allowing for adjustments in treatment before significant vision loss occurs.
Future of OCT in Ophthalmology
As OCT technology continues to evolve, its potential applications in ophthalmology are expanding. Researchers are working on improving the resolution even further, reducing the cost of devices, and enhancing the speed of imaging. The integration of OCT with artificial intelligence (AI) also holds promise for automating certain diagnostic processes, making the technology even more efficient and accessible.
In addition, advancements in portable OCT devices are expected to bring this powerful tool to more remote and underserved regions, improving global access to quality eye care.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has firmly established itself as a cornerstone of modern ophthalmology, offering invaluable insights into the structure and health of the eye. Whether it’s diagnosing retinal diseases, managing glaucoma, or planning surgeries, OCT has transformed the way ophthalmologists provide care. With its non-invasive nature, high-resolution imaging, and real-time results, OCT enhances the ability to detect, monitor, and treat eye conditions, ultimately improving outcomes for patients and preserving vision. As technology advances, the role of OCT in ophthalmology will only grow, continuing to shape the future of eye care for years to come. For those interested in deepening their understanding of OCT and its applications, enrolling in an ophthalmology course or exploring ophthalmology video lectures can provide comprehensive insights into this cutting-edge technology and its impact on the field.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is the role of OCT in ophthalmology?
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging method that uses reflected light to create pictures of the back of your eye. It helps eye care providers diagnose and manage common eye diseases like diabetes-related retinopathy and glaucoma.
- What is the role of OCT in neuro ophthalmology?
OCT allows non-invasive visualisation of the anatomy of the most anterior part of the visual pathway, from retina to lamina cribrosa. Lesions involving the pre-laminar area can be assessed with spectral domain (SD-OCT) and enhanced depth imaging OCT (EDI-OCT) of the ONH.
- What are the advantages of OCT?
Its main strength consists of the real-time three-dimensional visualization of tissue structure and function without the necessity for a sample biopsy. High resolution, fast image acquisition, improved image quality, artifact reduction, and versatility have made OCT an innovative imaging device over time.
- What is the role of OCT in optic neuritis?
OCT is a quick and non-invasive test that reveals important clinical information in patients with optic neuritis. Our study supports the use of OCT in the detection of remote optic neuritis, given its high sensitivity using the 99th percentile intereye difference as a cutoff.
Related post