Everything you need to know about Ophthalmology MD
The specialised area of medicine known as ophthalmology is dedicated to eyes’ health. It covers the physiology, anatomy, and disorders that could impact the eyes. A professional doctor who deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and medical care of the eyes is an ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists are trained in both surgical techniques and pharmacological therapies because this could involve both. M.D.s have the specialised training to offer the complete range of eye care, from performing intricate and delicate eye surgery to dispensing contact lenses and spectacles. Research into the causes and treatments for eye disorders and vision issues is another area of expertise for many eye doctors.
What does the PG Ophthalmology course focus on?
PG Ophthalmology programme lasts 3 years after students complete their MBBS degree. The course helps train students to treat eye conditions such as glaucoma, which damages the optic nerve and impairs vision, with the potential to result in blindness, iritis, which is an inflammation of the iris that may be caused by a systemic disease, chemical burns, orbital cellulite. Higher education and training in a variety of subspecialties are made available to enrolled students, from performing critical eye surgery to prescribing glasses and contact lenses. The course is well-structured for doctors to address any eye issues that may arise.
The course covers the fundamentals of ophthalmology as well as more complex topics such as disorders of the optical nerve system and the uvea and vitreoretinal tissues. According to analyses obtained through the use of medication, surgery, diet, and other therapies, doctors are taught how to cure eyes. The curriculum is developed to equip MD students with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide total eye care, including vision services, eye examinations, medical and surgical eye procedures, and the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders and other visual difficulties.
DigiNerve’s Ophthalmology MD Course by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna
Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna, the Editor-in-Chief of Ophthalmology MD has designed the course along with India’s 55 renowned faculty. Their collective expertise will help students remarkably to gain an in-depth knowledge of concepts. The course is designed from an academic, clinical, and surgical point of view. The in-video demonstration of various surgeries will give a whole new dimension to students’ postgraduate learning.
The Ophthalmology MD course is a thoughtfully compiled collection of topics from prominent ophthalmologists from across the nation. Around 400 topics that are significant from an academic, clinical, and surgical perspective are collected in the course. All of the course’s topics have been carefully chosen with consideration given to frequently asked questions and troublesome regions for postgraduate students to provide adequate knowledge.
This programme is one of the best PG Ophthalmology courses for students who are seeking to fare well in post-graduation. Components of the course appropriately match the requirement of students in the pre-operative workup, helping them to perform surgical skills and even handle post-operative difficulties. To meet all of the students’ learning needs, it promotes concept and approach-based learning.
Postgraduate students who are taking exams have a special section with an innovative examination corner. For frequently encountered ocular disorders, particular focus is placed on obtaining the proper clinical findings by following the proper case and history-taking procedures.
With the use of surgical videos combined with 3D animated sequences of every surgical step, practitioners could also develop clinical/surgical ophthalmic skills. The conceptual knowledge will take on a completely new dimension, thanks to the in-video display of the numerous surgeries being carried out.
To help students gain a full understanding of each topic and to prepare them for exams, the lectures are richly illustrated with clinical/surgical and radiological pictures, as well as flowcharts, tables, and boxes, wherever necessary. For many illnesses, recent evidence-based recommendations have been added to familiarise readers with recent developments in the field. The important diagnostic procedures and techniques have been covered in detail along with a drug chart for quick reference for the students with a special focus on drug dosages, adverse effects, and their indications/contraindications.
Table of Content – Ophthalmology MD by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna
Cataract
Lens
Anesthesia for Cataract Surgery
Preoperative Evaluation of Cataract Surgery
IOL Power Calculation
Ocular Viscosurgical Devices
Manual Extracapsular Cataract Extraction
Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery – Basics
Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery – Complications
Applications of Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery
Secondary IOL Implantation Through Sclero-Corneal
Phacodynamics
Phacoemulsification Techniques
Cortical wash – Coaxial and Bimanual Irrigation Aspiration Techniques
Foldable IOLs, Loading and Implantation
Complications of Phacoemulsification
Applications of Phacoemulsification
Repositioning of IOL and IOL Exchange
Femto Laser Assisted Cataract Surgery
Lens Induced glaucoma
Instrument Sterilization
Cornea
Cornea Basics
Corneal Topography
Specular Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy
Bacterial Keratitis
Fungal Keratitis
Acanthamoeba Keratitis
Microsporidial Keratitis
Herpes Simplex Keratitis
Herpes Zoster Keratitis
Non Healing Keratitis/Non Healing Corneal Ulcers
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis I -General concepts
Corneal Ectasia
Pterygium
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency
Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Chemical Injuries of the Eye
Limbal Epithelial Transplantation (SLET and CLET, Buccal)
Amniotic Membrane Transplantation
Keratoprosthesis
Management of Ocular Trauma
Contact Lens
Corneal retrieval and Eye banking
Penetrating keratoplasty
Therapeutic keratoplasty
Graft Rejection
Refractive Surgeries
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty
Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty
Glaucoma
The Angle of Anterior Chamber
Aqueous Humour Dynamics
Tonometry
Central Corneal Thickness and Glaucoma
Gonioscopy
Pathogenesis of Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy
Clinical Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head
Optic Nerve Head Changes in Glaucoma
Interpreting Humphrey Visual Field Reports
Interpreting Octopus Perimetry Reports
Anterior Segment Imaging Imaging – Ultrasound Biomicroscopy and Anterior segment Optical Coherence Tomography
Optic Nerve Head Imaging/Role of OCT in Glaucoma
Classification of the Glaucomas
Ocular Hypertension
Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
Primary Angle Closure Disease
Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma
Pigmentary Glaucoma
Lens Induced glaucoma
Uveitic Glaucoma
Neovascular Glaucoma
Glaucoma Associated with Ocular Trauma
Nanophthalmos and Other Secondary Angle Closure Glaucomas
Glaucoma after Vitreoretinal Surgery
Steroid Induced Glaucoma
Glaucoma following Penetrating Keratoplasty
Glaucoma Associated with Corneal Disorders
Classification and Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Glaucoma
Primary Congenital Glaucoma
Juvenile Open Angle Glaucoma
Glaucoma in Phacomatoses
Target Intra Ocular Pressure
Medical Management of Glaucoma
Newer Ocular Hypotensive Medications
Neuroprotection
Lasers in Glaucoma
Trabeculectomy
Glaucoma Drainage Devices
Non-Penetrating Deep Sclerectomy
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery
Cyclodestructive Procedures
Neuro-Ophthalmology
Practical Pearls in Neuro-ophthalmology
Neuro-ophthalmic Cases: Case Scenarios
Approach to Neuroimaging in Neuro-ophthalmology
Evaluation of a Case of Double Vision
Optic Neuritis
Optic Atrophy
Papilloedema
Myasthenia and Myopathies
Nystagmus-Evaluation
Double Vision A 10-step Assessment Plan
Myasthenia Gravis and its Mimickers
Neuro-Ophthalmic Examination: An Overview
MRI Making Sense of the Images
Neuroimaging for Ophthalmologists
Evaluation of a Pale Optic Disc
Optic Neuropathy
Pupil Pathways and Inference
Bilateral Ocular Motility Disorders – A Differential Diagnosis
An Approach to Swollen Optic Discs
Visual Fields in Neuro-ophthalmology
Ocular-Microbiology
Basic Microbiology
Antibiotics: Therapy and Testing
Molecular Diagnosis in Ocular Microbiology
Orbit
Anatomy of the Orbit
Lacrimal Apparatus
Imaging of the Orbit: Computed Tomography Scan
Orbital Decompression for Thyroid Orbitopathy
Proptosis- General Concepts
Orbital trauma- Considerations and principles
Orbital fractures and management
Orbit Infections
Fungal Infections of the Orbit
Parasitic Infections of the Orbit
Orbital Inflammations
Anophthalmic Socket
Contracted Socket
Benign tumors of the Orbit
Vascular Lesions of the Orbit
Reconstructive Socket Surgeries: Enucleation, Evisceration and Exenteration
Blepharoptosis: Evaluation and Management
Eyelid Retraction
Ectropion
Entropion
Esthetic Eyelid Surgery
Basics of Eyelid Reconstruction
Overview of Eyelid Reconstruction
Lacrimal Drainage System: Anatomy and Anomalies
Evaluation of the Lacrimal System
Congenital NasoLacrimal Duct Obstruction
Adult NasoLacrimal Duct Obstruction
Botulinum Toxin in Ophthalmology
Orbitotomy- Introduction
Lateral Orbitotomy
Orbitotomy – Other Approaches
Oncology
Pediatric Ophthalmology
Development of Visual System
Typical Development of Visual Milestones
Estimating Visual Acuity in a Child
Estimating Visual Acuity in Infant
Childhood Refractive Errors and Guidelines on Management
Lazy Eye
Red Eye in a Child and Vitamin A Deficiency
Syndromes with Ocular Manifestation
Low Vision (Visual Impairment)
Vision Assessment in Children with Low Vision
Low Vision Aids – Optical
Non Optical Aids and Rehabilitation
Headaches in Children
Ocular Causes of Headache
Retina
Macular Function Tests
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography
Indocyanine Green Angiography
Optical Coherence Tomography
OCT Angiography
USG + UBM
Fundus Autofluorescence and Multicolor Imaging
Retina
Anatomy, Physiology and Embryology of Vitreous
Evaluation of Retina and Vitreous
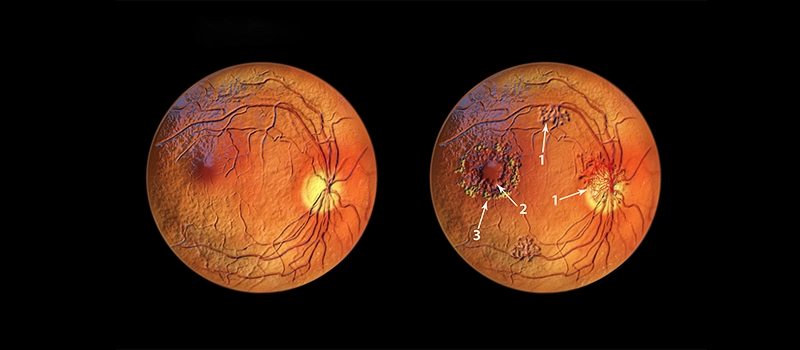
Diabetic Retinopathy
Hypertension and the Eye
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Pachychoroid Spectrum Disease – Introduction and Pachychoroid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Central Serous Chorio-Retinopathy
Pachychoroid Neovasculopathy & Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV)
Peripapillary Pachychoroid Syndrome & Focal Choroidal Excavation
Hereditary Macular Dystrophies
Macular Pathologies
Peripheral Retinal Degenerations
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Melanoma PG 1
Retinoblastoma
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy
Vascular Tumors of Retina and Choroid
Lasers in Retina
Intravitreal Injections
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Non Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Posterior Segment Trauma
Systemic Diseases with Retinal Manifestations
Principles of Vitreoretinal Surgery
IOFB and its Management
Endophthalmitis
AI in Ophthalmology
Vitreoretinal Interface Diseases of the Macula – Epiretinal Membrane
Strabismus
Extra-Ocular Muscles & Orbital Fascia Applied Anatomy
Physiology of Extra Ocular Muscles
Binocular Single Vision
Strabismus – Classification & Etiology
Approach to a Comitant Deviation Patient
Diplopia
Hess Charting
Comitant Horizontal Strabismus: Esodeviation
Comitant Horizontal Strabismus: Exodeviation-
Vertical Deviation a. Approach to vertical deviations
Pattern Strabismus
Paretic Strabismus
Diagnosis and Management of Oculomotor Palsy
Diagnosis and Management of Trochlear Nerve Palsy
Diagnosis and Management of Abducent Nerve
Duanes Retraction Syndrome
Restrictive Strabismus
Browns Syndrome
Monocular Elevation Deficiency
Thyroid Related Strabismus
Congenital Fibrosis of Extra Ocular Muscles
Non-surgical Management of Strabismus
Surgical Management of Strabismus
Complications of Strabismus Surgery
Uvea
Uveal Tract
The SUN Classification & Terminologies of Uveitis
Systematic Work Up in Uveitis
Construction of Differential Diagnosis in Uveitis
Art of Ordering Lab Investigations in Uveitis
Immunosuppressives and New Biologicals
Management of Uveitic Cataracts
Ocular Tuberculosis
Viral Anterior Uveitis
Viral Uveitis
CMV – Posterior Uveitis
Leptospirosis & Syphilitic Uveitis
Ocular Toxoplasma
HIV and Opportunistic Infections Non Infectious Uveitis
Autoimmune Diseases and Uveitis
Sarcoidosis
VKH
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
The Masquerades
Refraction
Visual Acuity
Refractive Errors
Retinoscopy
Subjective Refraction
Accommodation and Convergence
Presbyopia Mechanism, Optical Correction and Surgical Procedures
Spectacle Lenses, Frames and Vertex Distance
Bifocals/Trifocals
Progressive Additional Lenses
Prisms
Contact Lenses
Colour Vision Contrast Sensitivity and Higher Order Aberrations
Aberrometer
Keratometry
Lensometer
Low Vision Aids
Examination Corner
How to Write a Theory Paper
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Uveitis Case?
FAQs in a Uveitis Case
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Cornea Case
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Retina Case?
FAQs in a Fundus Case Pertaining to the Retinal Vessels
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Glaucoma Case?
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Orbit Case?
FAQs in a Orbit Case
How to Describe Management in Examinations
Investigations
OSCE Glaucoma
OSCE in Posterior Segment
OSCE in Neuro-ophthalmology
Ophthalmic Instruments
Best Way to Study Ophthalmology MD
- The postgraduate students should actively participate in lecture demonstrations, seminars, symposia, and inter and intradepartmental meetings. Through participation in symposia, CMEs, and journal clubs, they are exposed to contemporary developments. This will help them to focus on the aim, methods, remarks, conversations, and conclusions.
- They should gain clinical training by going through maximum clinical case discussions. Case discussions based on student-written patient records will assist students to hone their diagnostic and decision-making abilities.
- They should participate in presentations and discussions in a variety of ways. Using a problem-oriented approach will help students with decision-making.
- They should indulge in discussions with their senior postgraduate students before presenting in the symposium. The postgraduate students can prepare for a class-wide debate by participating in these discussions.
- Postgraduate students should indulge in bedside conversations during rounds and outpatient instruction which will help create an impact on patient management.
- Students should take interest in consultant’s case presentations which help in the solution of challenging issues and provide a forum for the debate of intriguing instances.
- The postgraduate students must take part in the training and instruction of interns and undergraduate students to brush up on their knowledge.
- They should attend monthly chat shows by eminent faculty, like the ones provided by the DigiNerve app.
- The student must take up rotations in the specialty clinics- Anterior segment and cataract, Glaucoma, Oculoplastics, Paediatric ophthalmology and strabismus, Retina and Uvea, Cornea, Contact lens and low vision, Neuro-ophthalmology, and Refractive Clinic.
- The postgraduate students should take the postings very seriously since they familiarize students with the typical ophthalmic issues. They must work freely and accept new and old cases, including refractions.
- The postgraduate student should make sure to keep an in-depth history and case record.
- MD students need to focus on basic sciences, biostatistics, research technique, teaching methodology, hospital waste management, health economics, medical ethics, and legal concerns connected to the practice of ophthalmology.
FAQs
Q1. What is the highest degree in ophthalmology?
Ans. Doctor of Medicine in Ophthalmology is the highest degree gained in the field of ophthalmology.Q2. What is the future of ophthalmology?
Ans. By 2025, there will be a need for about 22,000 ophthalmic surgeons, according to an estimate from the Health Resources and Services Administration in 2016. It also predicted that there will be more than 6,000 more doctors needed to meet the demand than there are currently available ophthalmologists.
Q3. What are the subspecialties in Ophthalmology?
Ans. Subspecialties in Ophthalmology include Glaucoma, Strabismus/pediatric ophthalmology, neuro-ophthalmology, anterior segment/cornea, retina/uveitis, oculoplastics/orbit, and ocular oncology.
Related post